r22 freon ac unit
At No Sweat AC & Heating, we understand how important saving time and money is for our clients. Instead of waiting for business hours to find out the answers to commonly asked questions, we provided the answers below. R22 (Freon) is what 95% of Americans currently use in their AC units to cool their homes. As of 2010, in response to EPA guidelines, units needing R22 (Freon) are no longer being produced. In place of R22 (Freon), units now utilize 410A (Puron). As a result of these changes, the price of R22 (Freon) has increased significantly. A system that uses R22 (Freon) cannot be refilled with 410A (Puron) gas. If a condenser or air handler stops working and cannot be repaired, the homeowner must replace the entire system with a system that uses 410A (Puron). SEER is an acronym for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio. Air handlers and condensers are each rated for efficiency. The total of those two rating numbers tells the total SEER rating of the system. The minimum Florida SEER standard is 13.

The higher the SEER rating, the more efficiently the system runs. However, there is a balance between cost and efficiency because the higher the SEER rating, the higher the cost as well. To discover what type of system you currently have in your home, go to the thermostat. If you have an emergency heat button, switch, or selection you likely have a heat pump system. If you only have cool off and heat button, switch, or selection you likely have a straight cool system.Air conditioning systems do more than just cool the air: They lower humidity and also remove dust, dirt and pollen by moving the air through filters and over the wet surface of the evaporator coils. The easiest, and often most effective, maintenance step is to regularly change or clean your air filter. When filters become clogged with dirt, the system must work harder to do its job of keeping your passengers comfortable on the most sweltering of summer days. Depending on the amount of dust in the air, filters can become clogged in just a short period of time.

Most late-model coaches have disposable filters that should be checked weekly and replaced when necessary. Earlier-model coaches have a cleanable screen that should be checked at routine intervals. A coach should never be operated without filters, which could lead to decreased system efficiency and a need for more frequent cleaning of the heat-exchanger coils.
home ac unit keeps tripping breaker Likewise, keeping the air-conditioning unit free of debris and blockage is vital to maintaining proper airflow and efficient heat removal.
18000 btu air conditioner split systemClean air can also reduce load and wear on the blower motors, extending their service life.
panasonic cube ac outdoor unit But filters and debris-removal aren't the only story.

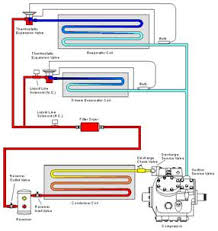
One of the most overlooked aspects of the air conditioning system is the freon itself and what it means to the air-conditioning system. A refrigerant can be any substance that will transfer heat from one location to another. In liquid form, a refrigerant will absorb heat when it evaporates; it is this conditional change that produces the cooling effect in the refrigeration process. When the vapor is changed back into a liquid through the process of condensation, heat is again moved, this time out of the freon. The word 'freon' is actually a trademarked name, but is often used to refer to any refrigerant gas used in a refrigeration process system. R134a and R22 are the two most common refrigerants used today, due to their respective boiling points and heat-carrying properties. The compressor compresses cool freon gas, causing it to become hot, high-pressure gaseous freon. This hot gas runs through a set of coils so it can dissipate its heat load into the surrounding air, and it condenses into a liquid.

The liquid freon then runs through an expansion valve that reduces the pressure suddenly, and in the process it becomes cold, low-pressure freon liquid. This cold liquid runs through coils that allow the freon to absorb heat from the air supplied by the blowers and evaporate back into a gaseous state. The now cooler air is then blown into the passenger compartment. The freon level is a major factor in maintaining not only the temperatures of the HVAC cycle, but also in maintaining system pressures. These operating pressures become one of our most valuable diagnostic tools for an AC system. Most coaches use receiver tanks as storage devices to separate the gaseous and liquid freon. The gaseous freon stays at the top, and the liquid freon settles to the bottom, where it is delivered to the thermal expansion valve. The thermal expansion valve is designed to meter liquid freon, and must receive only liquid freon. If the expansion valve doesn't meter correctly, it will flood or starve the evaporator.

If the expansion valve receives vapor instead of liquid from the receiver tank, as it would from a low refrigerant level, the evaporator will starve. Since there can be no vaporizing and heat transfer in the evaporator if that condition occurs, pressure levels are also affected. It will also cause the evaporator to work harder because the freon, already in a gaseous state, can't change states and absorb heat from the air. This puts a larger load on the system and impairs its capacity to cool. If the evaporator is flooded with liquid, the evaporator can't vaporize all of the refrigerant; in turn, liquid freon can escape into the compressor, where it can saturate the compressor and make it work harder. As the compressor attempts to compress the liquid freon (an impossibility), the buildup of heat and pressure can damage the compressor. Having too much freon in an air-conditioning system also creates problems. It increases the pressure and temperature, inside the system because the freon has less space to change states, which also reduces cooling efficiency.