ac unit btu chart

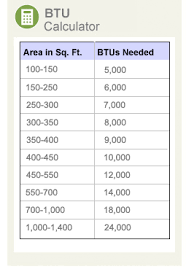
How do I choose which BTU air conditioner? Air conditioner capacity is measured by "BTU". BTU stands for British Thermal Units. Follow the table below to find the approximate ideal cooling capacity (btu) Eco-Air air conditioner for your room: Shaded room N/E facing Sunny room S/W facing & conservatories The above recommendations are estimates based on Eco-Air's air conditioning units only. Most Eco-Air air conditioners have both cooling and heating capabilities. Eco-Air's Plasma Dust Collector can generate an ionization zone. The air is converted to plasma as it passes the high voltage ion generator. 95% of dust, smoke and pollen particles are attracted to the electrostatic filter. Ideal for those who are looking for clean, fresh pollen free air. This is a favourite with hay fever sufferers and smokers. All split air conditioning units contain F Gas and is govern by F-Gas regulations. All F-Gas units must be handle by qualified F-Gas engineers. Portable Air Conditioning |

Air Conditioning Installation | Unit 7, Propeller Park, 400 North Circular Road, London NW10 0AB | © ECOAIR All Rights Reserved | Terms & conditions | Do you know what size your air conditioner is? In the world of building science, you'll hear a lot of talk about why oversized air conditioners are a bad idea. Briefly, they may not dehumidify as well, short-cycling wears them out quicker, and your home will probably be less comfortable if the air conditioner is too big. But to know if your AC is oversized, first you have to know what size it is. (Note: This article is about finding the size of your existing AC, not determining what size you need.) Look for the label The good news is that most HVAC manufacturers make it easy to determine the nominal capacity of your air conditioner. It's in the model number. Go outside and find the outdoor unit, that metal noisemaker hidden away on the side or the back of the house. It'll look something like the one you see above, although maybe not quite so decrepit as that one.

Then find the lable that gives the data about your AC. It'll look like the image below. Up near the top of the label, you see the model number (M/N) and serial number (S/N). The model number is where you can find the number you're looking for. Not all manufacturers do this, but most will give you a 2 or 3 digit section that tells you how many thousands of BTU/hour your air conditioner can move out of your home.
3 ton air handler heat pump The first section in the model number gives you info about the type and efficiency of the unit you're looking at.
2001 honda civic ac compressor bearingIn the case of this Lennox model (which, by the way, is not from the outdoor unit shown at the top of this article), the 13HPX tells you it's a heat pump with an efficiency rating of 13 SEER.
home ac unit sweating
The digits you need Just past that string of 5 characters, though, is the part that tells you the nominal size: 048. That means the air conditioner—or heat pump in cooling mode in this case—has a nominal capacity of 48,000 BTU/hour. I say nominal because the actual capacity is almost certainly going to be different. The numbers you'll see on residential air conditioners and heat pumps are: The 3 digits in the model number tell you the nominal capacity in thousands of BTU/hr. Since each 12,000 BTU/hr is equivalent to 1 ton of air conditioner capacity, it's easy to figure out how many tons of nominal capacity your AC has. Why Is Air Conditioner Capacity Measured in Tons? 3 Reasons Your 3 Ton Air Conditioner Isn't Really 3 Tons Why an Oversized Air Conditioner Is a Bad Idea NOTE: Comments are moderated. Your comment will not appear below until approved.For other uses, see BTU (disambiguation). The British thermal unit (BTU or Btu) is a traditional unit of work equal to about 1055 joules.

It is the amount of work needed to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. One four-inch wooden kitchen match consumed completely generates approximately 1 BTU. In science and engineering, the joule, the SI unit of energy, has largely replaced the BTU. The BTU/h is most often used as a measure of power in the electric power, steam generation, heating, and air conditioning industries. It is still used in some metric English-speaking countries (such as Canada, but notably not the United Kingdom).[] In North America, the heat value (energy content) of fuels is often expressed in BTUs. The notation kBtu or KBTU is often used for thousand BTU, in sizing of heating systems and in the Energy Use Index (EUI) expressed as thousand BTU annual energy use per square foot of building. MBTU represents one million Btu, although the atypical notation MMBtu or mmBtu is sometimes used to represent one million BTU. A BTU is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 avoirdupois pound of liquid water by 1 degree Fahrenheit at a constant pressure of one atmosphere.
[1] As with the calorie, several definitions of the BTU exist, because the temperature response of water to heat energy is non-linear. This means that the change in temperature of a water mass caused by adding a certain amount of heat to it will be a function of the water's initial temperature. Definitions of the BTU based on different water temperatures can therefore vary by up to 0.5%. The unit MBtu or mBtu was defined as one thousand BTU, presumably from the Roman numeral system where "M" or "m" stands for one thousand (1,000). This notation is easily confused with the SI mega- (M) prefix, which denotes multiplication by a factor of one million (×106), or with the SI milli- (m) prefix, which denotes division by a factor of one thousand (×10−3). To avoid confusion, some companies and engineers use the notation "MMBtu" or "mmBtu" to represent one million BTU. Alternatively, the term therm may be used to represent 100,000 (or 105) BTU, and quad for 1015 BTU. Some companies also use 'BtuE6' in order to reduce confusion between 103 BTU and 106 BTU.

A BTU can be approximated as the heat produced by burning a single wooden kitchen match[5] or as the amount of energy it takes to lift a one-pound weight 778 feet (237 m). When used as a unit of power for heating and cooling systems, BTU per hour (BTU/h) is the correct unit, though this is often abbreviated to just "BTU". The BTU should not be confused with the Board of Trade Unit (B.O.T.U.), which is a much larger quantity of energy (1 kW·h or 3,412 BTU). The BTU is often used to express the conversion-efficiency of heat into electrical energy in power plants. Figures are quoted in terms of the quantity of heat in BTU required to generate 1 kW·h of electrical energy. A typical coal-fired power plant works at 10,500 BTU/kW·h, an efficiency of 32–33%. ^ International standard ISO 31-4:1992 Quantities and units—Part 4: Heat ^ Btu - Kilocalories units conversion ^ 2009 ASHRAE Handbook – Fundamentals (I-P Edition). American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc